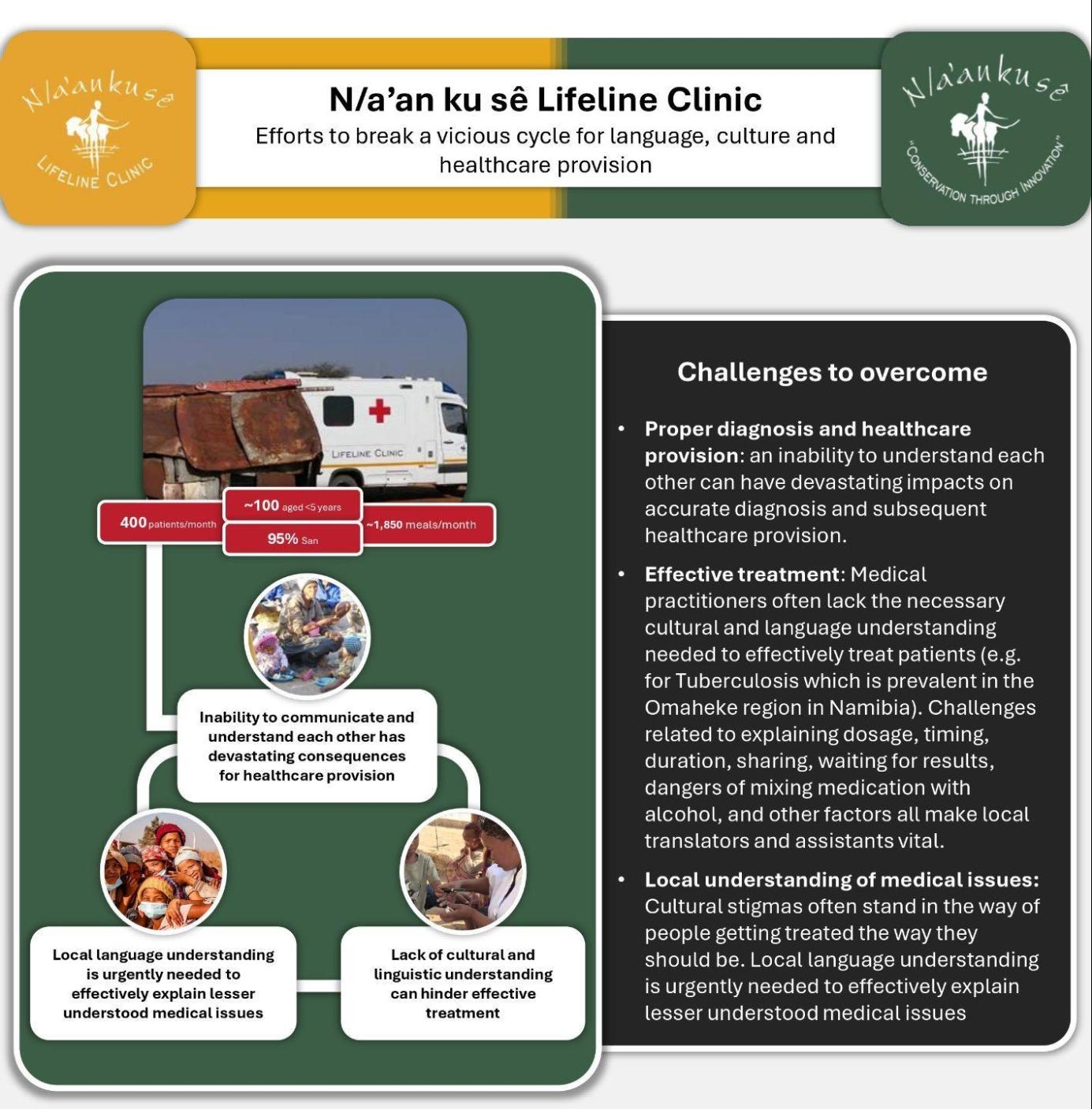
Challenges






The ability to use indigenous languages and traditional practices directly affects the wellbeing of community members. Thus it is imperative that multilingualism and multi-culturalism are embraced to offer better health provision, recognizing traditional systems of medicine, as well as promoting social cohesion and delivering humanitarian responses, especially during health crises, and natural disasters.






Efforts to break a vicious cycle for language, culture and healthcare provision